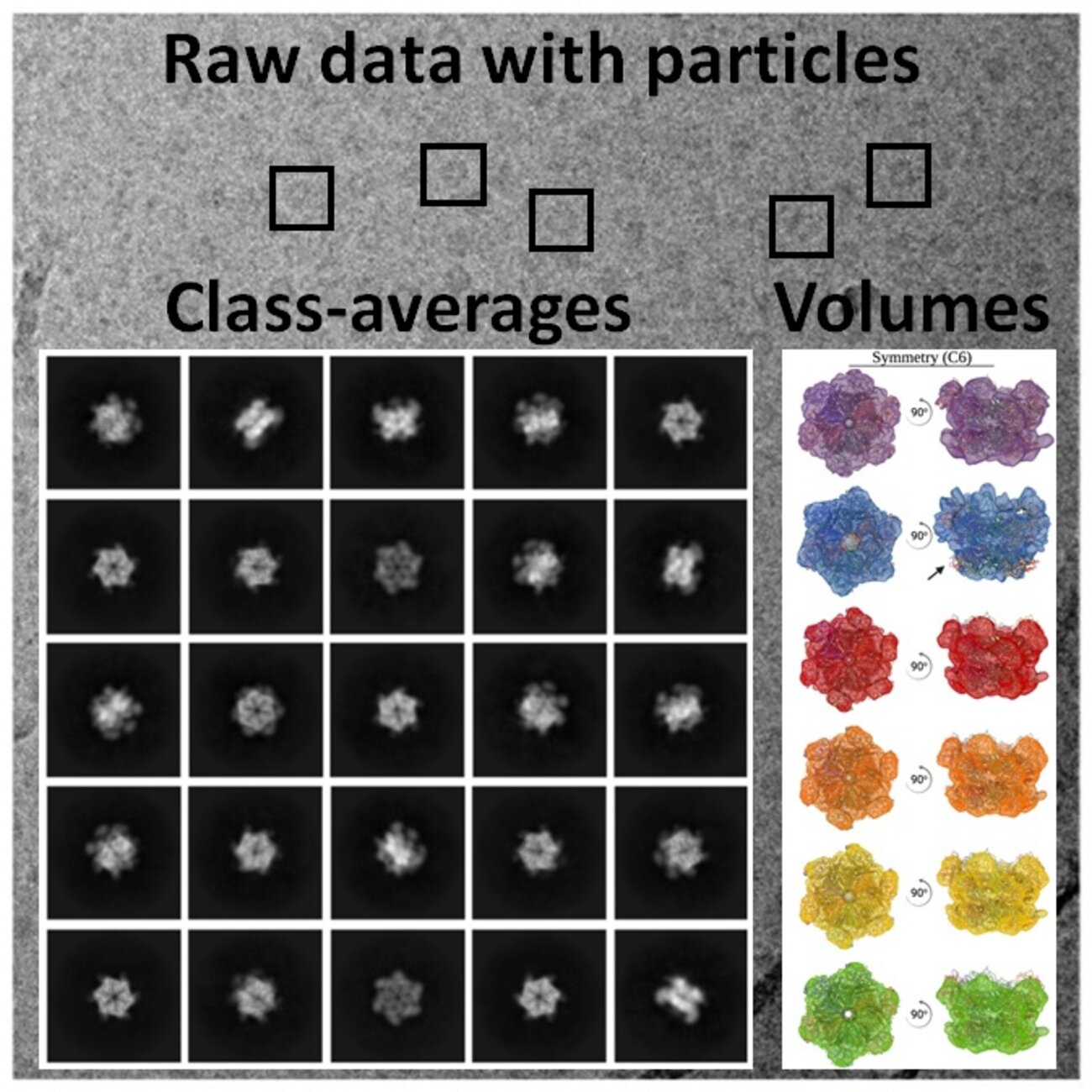
Electron Microscopy
There are three basic concepts (modalities) of electron-beam imaging and analysis: transmission (TEM), scanning transmission (STEM) and scanning (SEM) electron microscopy. Various imaging modes make use of differently generated signals after the primary electron beam has interacted with the specimen. Additional analytical information is available by current flow, diffraction (on crystallographic parameters), by spectroscopy (on chemcial composition) and by photons (chemical – electronic state).
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy use the various information carried by electrons transmitting a thin sample. more
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Scanning electron microscopy uses the wealth of information carried by elastically or inelastically backscattered electrons. more
Cryo-EM
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) is applied to beam sensitive samples cooled (vitrified) to cryogenic temperatures. Along with applications in softmatter, it has become one of the main techniques of structural biology. It allows obtaining structural information ranging from molecular to cellular level. This technique is crucial for detailed structural-functional characterization of biological samples in near native state. more

Volume EM
The term ‘volume electron microscopy (vEM)’ describes a group of powerful techniques used to obtain comprehensive three-dimensional information about the internal structures of materials or biological specimens at nanometer resolution. more