EDS/WDS
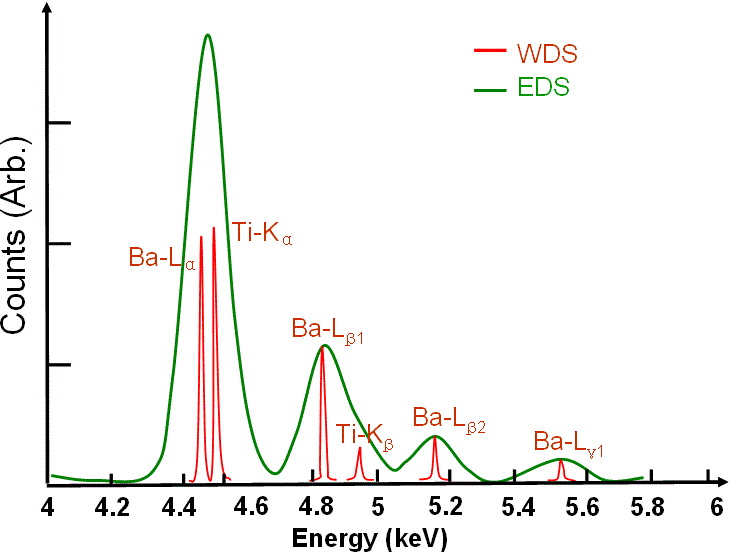
EDS is a non-destructive technique that allows for the elemental analysis of a sample. One of its primary advantages is its speed and ease of use, as it provides a rapid assessment of the elemental composition of a sample. EDS is also well-suited for examining large and irregularly shaped samples, making it a versatile choice. However, EDS has limitations when it comes to detecting low atomic number elements and distinguishing between elements with similar atomic numbers, which can lead to inaccuracies in the results.
On the other hand, WDS is a technique known for its superior spectral resolution and accuracy in quantifying elemental concentrations. It excels at differentiating between elements with close atomic numbers and is particularly useful for trace element analysis. However, WDS is more time-consuming, requiring precise instrument calibration and longer data acquisition times. Additionally, it is less suitable for examining non-conductive or beam-sensitive samples due to its higher energy electron beam requirements.
In summary, EDS offers speed and versatility but may struggle with certain elemental distinctions, while WDS provides exceptional accuracy but demands more time and specialized conditions, making the choice between them dependent on the specific analytical needs and constraints of the study.